7 Casing Capacity
Nomenclature | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Volume | Vol | Open Hole | OH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barrel(s) | bbl | Gallon | gal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Length | L | Q | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Width | W | Strokes per Minute | SPM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depth | d | Stroke | STK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
pi (3.14159265) | p | Stroke Length | LSTK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Height | h | Pump Efficiency | E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Radius | R | Pump Liner Inside Diameter | IDLINER | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diameter | D | Pump Rod Diameter | ODROD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(inside) | ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(outside) | OD | 1. Mud System Volume - The total mud system volume may be calculated with the drill string either in or out of the hole. Total Mud Volume = Pit Volume + Hole Volume 2. Pump Output Volume - Pump output tables must be adjusted for estimated or measured pump efficiencies. Triplex pumps usually have an efficiency between 90-98%. Double action duplex pumps usually have an efficiency between 85-95%. The following two equations calculate pump output at 100% volumetric efficiency. The constant, K, may be changed to obtain units of bbl/STK, gal/STK, or Liter/STK.
3. Mud Pit Volume - The same capacity equations shown in Dilution of Water-Based Muds hold true for volume. Depth will be the actual depth of mud in the mud pits. Capacity (Mud Pits) 1. Rectangular Mud Pits L = Length, ft W = Width, ft h = Height, ft 2. Sloping Sided Mud Pits
R2 arccos 57.296
Note: Calculator must be set for degrees for above equation. If you wish to use radians on the calculator, simply remove (57.296) from the above equation. 4. Upright Cylindrical Mud Pits Capacity and Displacement (Drill String and Hole)
1. Capacity - Capacity, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and other tubulars is the volume of fluid the pipe can contain. The internal pipe diameter, ID, (inches) is used in the equation shown below. Capacity of a wellbore, either cased or open hole, is the volume of fluid the hole can contain. The hole diameter, Dh, or casing ID are used in the equation above. 2. Displacement a. Open-End Pipe - Displacement, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and tubulars is the volume of fluid that the pipe will displace if placed into fluid open ended to allow it to fill inside. The displacement volume equals the volume of metal in the pipe. The pipe's outside diameter, OD, and inside diameter, ID, are used in the equation below. Displacement/OE, bbl/ft (OD)2-(ID)2-] 1029:4 3. Closed-End Pipe - Displacement, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and tubulars is the volume of fluid that the pipe will displace if placed into fluid with the lower end closed to allow no fluid inside. The pipe's outside diameter, OD, is used in the equation below. 1029.4 Annulus Capacity and Multiple-Pipe Annulus Capacity 1. Annulus Capacity -Annulus capacity, (Anncap) is the volume contained between two cylinders - one inside the other, such as casing with drill pipe inside. The casing ID, drill pipe OD are used in the calculation. Annulus capacity, bbl/ft = [(-D),-.-„iOD') -y y 1029.4 Annulus capacity of pipe or casing in an open hole of diameter, Dh, is calculated using Dh (instead of ID) and OD of the pipe or casing using the equation above. 2. Multiple-Pipe Annulus Capacity -An annulus may contain more than one pipe inside a casing or open hole. To calculate the fluid volume in a multiple annulus use the equation below, which assumes all pipes are the same OD (n = number of pipes in annulus.) When interior pipes are of different sizes, the individual ODs must be squared and summed and the sum subtracted from the ID2 value in the numerator of equation below. Multiple annulus capacity, bbl/ft = [(ID)2~'(OD)2] K 1029.4 For an open hole with multiple pipes, annulus capacity is calculated based on hole diameter, Dh in equation above, substituting Dh for ID. Conversion to Other UnitsBelow are equations that allow annulus capacity and displacement volume calculations to be made in other useful units. In these equations, 'D' represents the larger diameter and 'd' represents the smaller diameter. gal/ft = ( D2 - d2)( 0.0408 )
bbl/ft = ( D2 - d2)( 0.0009714 ) ft3/ft = (D2 - d2)(0.005454) ft/ft3 = ----1---8---3---.--3----5----- Note: For multiple-pipe annulus volumes substitute the value n(d2) for d2 in equations above when pipes are all same diameter. If not all same diameter, the OD of each pipe must be squared, summed and the sum subtracted from the value of ID2 in the numerator of the appropriate equation above. Tabulated Capacity and Displacement Data Tabulated values for capacity and displacements of various sizes, weights and tool-joint tubular goods is found in the Appendix of this Manual. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
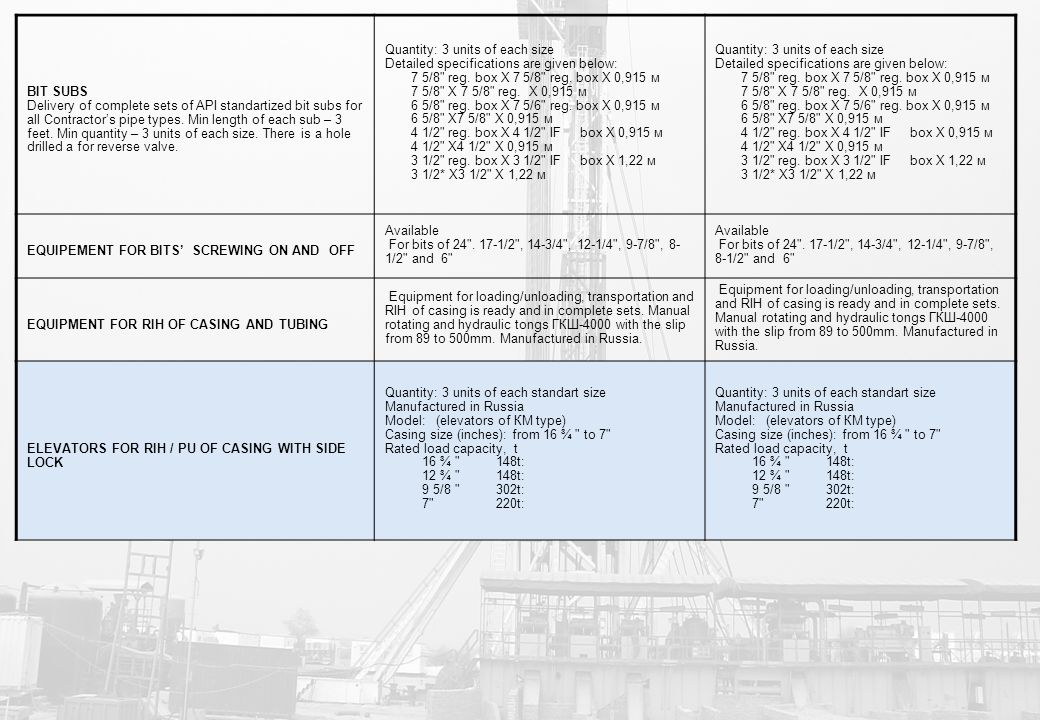
API Casing Data Tables Sizes 7.000 - 7.625. Specification 5C3 of the American Petroleum Institute standardizes 14 casing sizes from 4.5 inches (11.43 cm) to 20 inches (50.80 cm) outside diameter ('OD'). This and related API documents also promulgate standards for the threaded end finish, the wall thickness (several are available in each size to. 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 5/8 7 5/8 7 5/8 7 5/8 7 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 8 5/8 pe ben meTRIC guIDe - CASIng SIZe in. O.D mm lb/ft kg/m in. Mm 9.5 10.5 11.6 13.5 15.1 11.5 13.0 15.0 18.0 14.0 15.5 17.0 20.0 23.0 20.0 24.0 28.0 32.0 17.0 20.0 23.0 26.0 29.0 32.0 35.0 38.0 24.0 26.4 29.7 33.7 39.0 24.0 28.0 32.0 36.0 40.0 44. Table 7.5: Ranges of dn/t for Collapse Pressure Regions when axial stress is zero (usually we assume yield strength collapse). Table 7.6 Minimum performance of tubing given OD, Nominal weight and API Grade. Figure 7.13 (same as equation 7.11): Ellipse of plasticity. In casing design, we are concerned only with detrimental effects. Capacity (bbl/ft) Casing Data Sheet Collapse Pressure (psi) Grade Nominal Weight T & C lbs/ft O.D. (inch) Body Yield 1000 lbs Wall (inch) I.D. (inch) Drift Diameter (inch) Internal Yield Pressure Minimum Yield (psi) Joint Strength 1000 lbs 5 13 K-55 4140 4870 4870 4870 4870 186 201 309 208 0.253 4.4 94 4.369 0.00467 0.01962. The resulting case has significantly more capacity than any conventional belted magnum. Compared to the 7mm Remington Magnum, top 7mm RUM loads deliver 25% more energy at 300 yards. citation needed Such performance demands a price and in this case, that.
Continue reading here: Pressures


Was this article helpful?
Nomenclature | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Volume | Vol | Open Hole | OH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barrel(s) | bbl | Gallon | gal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Length | L | Q | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Width | W | Strokes per Minute | SPM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depth | d | Stroke | STK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
pi (3.14159265) | p | Stroke Length | LSTK | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Height | h | Pump Efficiency | E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Radius | R | Pump Liner Inside Diameter | IDLINER | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diameter | D | Pump Rod Diameter | ODROD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(inside) | ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(outside) | OD | 1. Mud System Volume - The total mud system volume may be calculated with the drill string either in or out of the hole. Total Mud Volume = Pit Volume + Hole Volume 2. Pump Output Volume - Pump output tables must be adjusted for estimated or measured pump efficiencies. Triplex pumps usually have an efficiency between 90-98%. Double action duplex pumps usually have an efficiency between 85-95%. The following two equations calculate pump output at 100% volumetric efficiency. The constant, K, may be changed to obtain units of bbl/STK, gal/STK, or Liter/STK.
3. Mud Pit Volume - The same capacity equations shown in Dilution of Water-Based Muds hold true for volume. Depth will be the actual depth of mud in the mud pits. Capacity (Mud Pits) 1. Rectangular Mud Pits L = Length, ft W = Width, ft h = Height, ft 2. Sloping Sided Mud Pits
R2 arccos 57.296
Note: Calculator must be set for degrees for above equation. If you wish to use radians on the calculator, simply remove (57.296) from the above equation. 4. Upright Cylindrical Mud Pits Capacity and Displacement (Drill String and Hole)
1. Capacity - Capacity, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and other tubulars is the volume of fluid the pipe can contain. The internal pipe diameter, ID, (inches) is used in the equation shown below. Capacity of a wellbore, either cased or open hole, is the volume of fluid the hole can contain. The hole diameter, Dh, or casing ID are used in the equation above. 2. Displacement a. Open-End Pipe - Displacement, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and tubulars is the volume of fluid that the pipe will displace if placed into fluid open ended to allow it to fill inside. The displacement volume equals the volume of metal in the pipe. The pipe's outside diameter, OD, and inside diameter, ID, are used in the equation below. Displacement/OE, bbl/ft (OD)2-(ID)2-] 1029:4 3. Closed-End Pipe - Displacement, as related to drill pipe, drill collars and tubulars is the volume of fluid that the pipe will displace if placed into fluid with the lower end closed to allow no fluid inside. The pipe's outside diameter, OD, is used in the equation below. 1029.4 Annulus Capacity and Multiple-Pipe Annulus Capacity 1. Annulus Capacity -Annulus capacity, (Anncap) is the volume contained between two cylinders - one inside the other, such as casing with drill pipe inside. The casing ID, drill pipe OD are used in the calculation. Annulus capacity, bbl/ft = [(-D),-.-„iOD') -y y 1029.4 Annulus capacity of pipe or casing in an open hole of diameter, Dh, is calculated using Dh (instead of ID) and OD of the pipe or casing using the equation above. 2. Multiple-Pipe Annulus Capacity -An annulus may contain more than one pipe inside a casing or open hole. To calculate the fluid volume in a multiple annulus use the equation below, which assumes all pipes are the same OD (n = number of pipes in annulus.) When interior pipes are of different sizes, the individual ODs must be squared and summed and the sum subtracted from the ID2 value in the numerator of equation below. Multiple annulus capacity, bbl/ft = [(ID)2~'(OD)2] K 1029.4 For an open hole with multiple pipes, annulus capacity is calculated based on hole diameter, Dh in equation above, substituting Dh for ID. Conversion to Other UnitsBelow are equations that allow annulus capacity and displacement volume calculations to be made in other useful units. In these equations, 'D' represents the larger diameter and 'd' represents the smaller diameter. gal/ft = ( D2 - d2)( 0.0408 )
bbl/ft = ( D2 - d2)( 0.0009714 ) ft3/ft = (D2 - d2)(0.005454) ft/ft3 = ----1---8---3---.--3----5----- Note: For multiple-pipe annulus volumes substitute the value n(d2) for d2 in equations above when pipes are all same diameter. If not all same diameter, the OD of each pipe must be squared, summed and the sum subtracted from the value of ID2 in the numerator of the appropriate equation above. Tabulated Capacity and Displacement Data Tabulated values for capacity and displacements of various sizes, weights and tool-joint tubular goods is found in the Appendix of this Manual. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 Casing Data
Continue reading here: Pressures
7 Casing Capacity Definition

Was this article helpful?